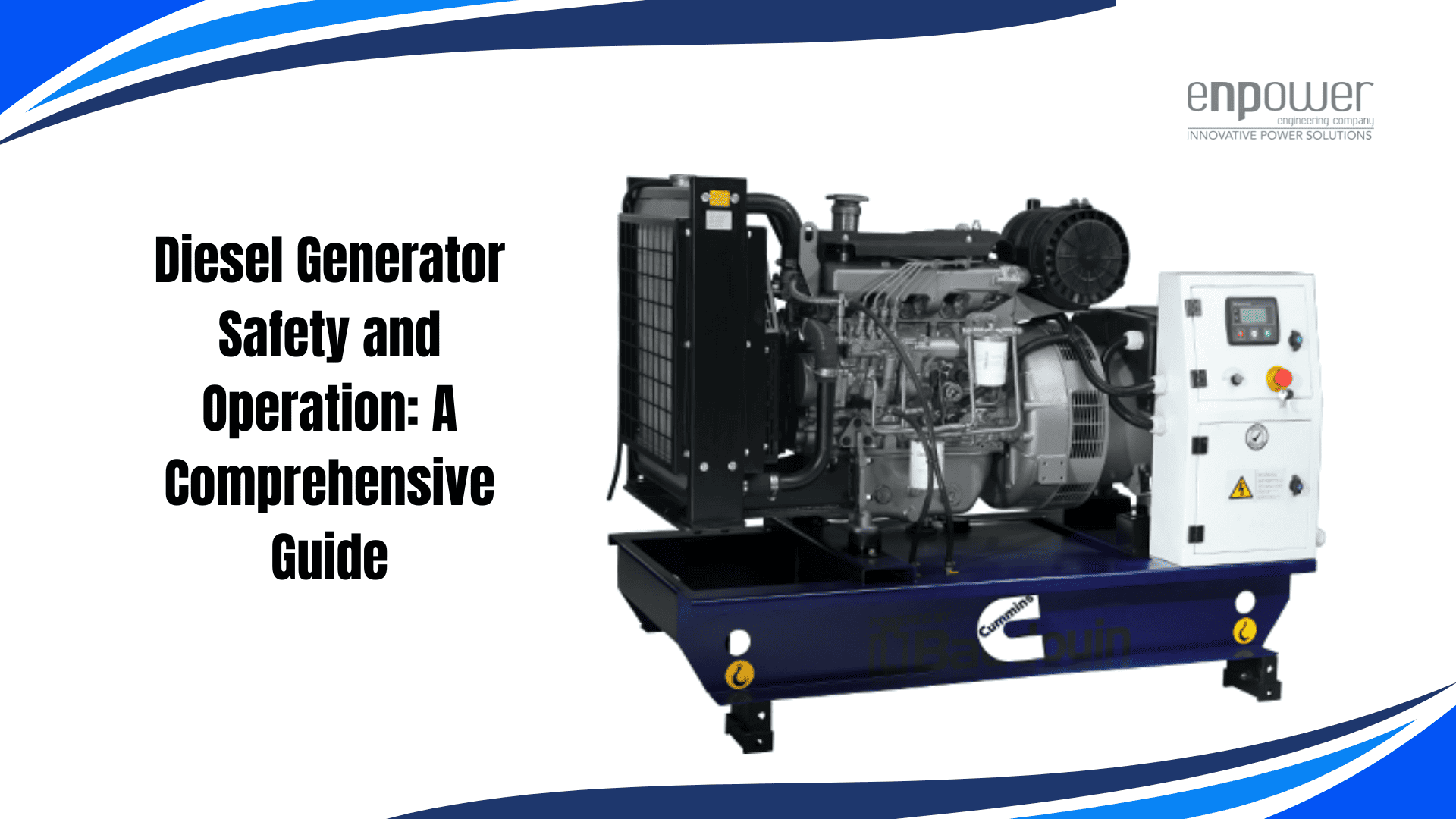
When it comes to reliable power backup, diesel generators are a popular choice. However, ensuring their safe operation is crucial. This comprehensive guide covers everything you need to know about diesel generator safety and operation.
Understanding Diesel Generators
What is a Diesel Generator?
A diesel generator converts mechanical energy into electrical energy using a diesel engine. These generators are commonly used for backup power in homes, businesses, and industrial applications.
Key Components of a Diesel Generator
- Engine: The core component that burns diesel fuel to produce mechanical energy.
- Alternator: Converts mechanical energy into electrical energy.
- Fuel System: Stores and supplies diesel fuel to the engine.
- Cooling System: Prevents overheating by dissipating excess heat.
- Exhaust System: Expels exhaust gases produced during combustion.
- Control Panel: Manages the generator’s operations and monitors performance.
- Battery: Provides the initial power to start the generator.
Safety Precautions for Diesel Generators
Proper Installation
- Location: Install the generator in a well-ventilated area away from living spaces to prevent carbon monoxide poisoning.
- Foundation: Ensure the generator is placed on a stable, non-combustible surface.
- Clearances: Maintain adequate clearances around the generator for safe operation and maintenance.
Regular Maintenance
- Scheduled Inspections: Conduct regular inspections to identify and address potential issues.
- Oil and Filter Changes: Replace oil and filters according to the manufacturer’s recommendations.
- Fuel System Checks: Inspect the fuel system for leaks and ensure clean fuel is used.
Safe Operation Practices
- Load Management: Avoid overloading the generator to prevent damage and ensure efficient operation.
- Starting and Stopping: Follow the manufacturer’s procedures for starting and stopping the generator.
- Fuel Handling: Store and handle diesel fuel safely to avoid spills and fire hazards.
Emergency Preparedness
- Emergency Shutdown: Know how to shut down the generator quickly in case of an emergency.
- Fire Extinguishers: Keep fire extinguishers nearby and ensure they are suitable for fuel fires.
- First Aid Kit: Have a first aid kit accessible in case of accidents.
Operational Guidelines for Diesel Generators
Starting the Generator
- Pre-Start Inspection: Check fuel levels, oil levels, and battery charge.
- Warm-Up: Allow the generator to warm up for a few minutes before applying the load.
Load Management
- Balanced Load: Distribute the electrical load evenly to avoid overloading any single circuit.
- Gradual Loading: Apply loads gradually to prevent sudden spikes that could damage the generator.
Monitoring Performance
- Control Panel: Regularly monitor the control panel for any warning lights or abnormal readings.
- Temperature and Oil Pressure: Keep an eye on the engine temperature and oil pressure to ensure they remain within safe limits.
Shutting Down the Generator
- Unload Gradually: Gradually reduce the load before shutting down the generator.
- Cool Down: Allow the generator to run without load for a few minutes to cool down.
- Turn Off: Follow the manufacturer’s procedure for turning off the generator.
Common Issues and Troubleshooting
Starting Problems
- Battery Issues: Check the battery for charge and connections.
- Fuel Problems: Ensure there is enough fuel and that the fuel is not contaminated.
Overheating
- Cooling System: Check for coolant levels and proper functioning of the cooling system.
- Ventilation: Ensure there is adequate ventilation around the generator.
Low Power Output
- Fuel Quality: Use clean, high-quality diesel fuel.
- Air Filters: Replace clogged air filters to ensure proper airflow.
Environmental Considerations
Emissions Control
- Exhaust System Maintenance: Regularly inspect and maintain the exhaust system to minimize emissions.
- Emission Standards: Ensure the generator meets local emission standards and regulations.
Noise Reduction
- Soundproof Enclosures: Use soundproof enclosures to reduce noise levels.
- Regular Maintenance: Keep the generator well-maintained to minimize noise from vibrations and mechanical issues.
Fuel Storage and Handling
- Spill Prevention: Use proper containers and procedures to prevent fuel spills.
- Storage Regulations: Follow local regulations for storing diesel fuel safely.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Can I run a diesel generator indoors?
No, running a diesel generator indoors is dangerous due to the risk of carbon monoxide poisoning. Always operate it in a well-ventilated outdoor area.
How often should I perform maintenance on my diesel generator?
Regular maintenance should be performed according to the manufacturer’s guidelines, typically every 200–300 hours of operation or annually, whichever comes first.
What should I do if my generator overheats?
If your generator overheats, shut it down immediately and check the cooling system for issues. Ensure the generator is placed in a well-ventilated area.
How can I reduce the noise from my diesel generator?
To reduce noise, use soundproof enclosures, place the generator on a vibration-absorbing surface, and ensure it is well-maintained.
Is it safe to refuel the generator while it is running?
No, refueling a running generator can lead to fuel spills and fire hazards. Always turn off the generator and allow it to cool down before refueling.
What should I do in case of a fuel spill?
In case of a fuel spill, contain the spill immediately, clean the affected area, and dispose of contaminated materials properly. Follow local regulations for handling and disposing of hazardous materials.
Can I use biodiesel in my diesel generator?
Check the manufacturer’s recommendations before using biodiesel. Some generators are compatible with biodiesel, while others are not. Using the wrong type of fuel can damage the engine.
How can I ensure my generator is ready for an emergency?
Perform regular maintenance, keep the fuel tank full, and conduct periodic test runs to ensure the generator is in good working condition and ready for use during an emergency.
What is the lifespan of a diesel generator?
The lifespan of a diesel generator can vary based on usage, maintenance, and operating conditions. With proper care, a diesel generator can last 10,000–30,000 hours of operation or more.
Are there any regulations for installing a diesel generator?
Yes, there are regulations for installing diesel generators, including location, noise levels, emissions, and safety standards. Consult local authorities and follow the manufacturer’s guidelines to ensure compliance.